Effective Treatments for Scalp Psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and scaly patches on the scalp. This guide provides an overview of its causes, symptoms, and effective treatments.
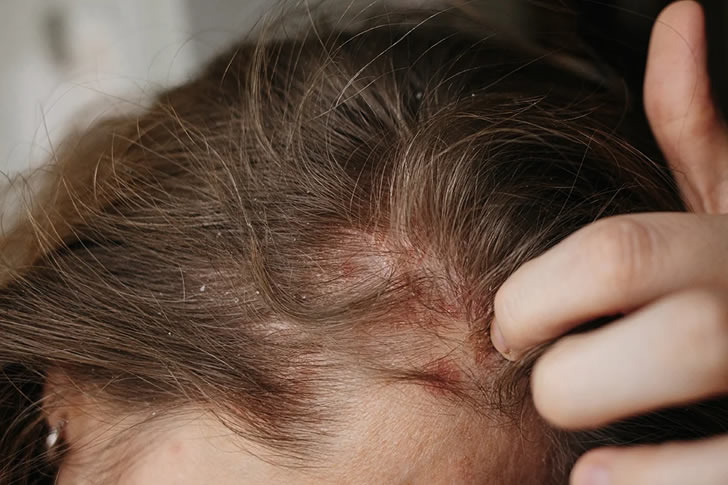
What is Scalp Psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis is a common form of psoriasis that affects the scalp. It can extend to the forehead, back of the neck, and around the ears. This condition occurs when the immune system triggers an overproduction of skin cells, leading to thick, scaly patches.
Causes of Scalp Psoriasis
The exact cause of scalp psoriasis is not fully understood, but it involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Key factors include:
- Genetics: A family history of psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Immune System: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
- Triggers: Common triggers include stress, infections, skin injuries, and certain medications.
Symptoms of Scalp Psoriasis
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include:
- Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
- Itching and discomfort
- Dry scalp that may crack and bleed
- Temporary hair loss due to scratching and inflammation
Diagnosis
A dermatologist can diagnose scalp psoriasis through a physical examination and, in some cases, a skin biopsy to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
- Topical Treatments: These are applied directly to the scalp and are often the first line of treatment.
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and slow down skin cell production.
- Vitamin D Analogues: Slow skin cell growth and remove scales.
- Coal Tar: Helps reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation.
- Salicylic Acid: Promotes the shedding of dead skin cells and reduces scaling.
- Medicated Shampoos: Over-the-counter and prescription shampoos containing ingredients like coal tar, salicylic acid, and ketoconazole can help manage symptoms.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can slow down the rapid skin cell turnover. Options include:
- UVB Light Therapy: Narrowband UVB light is effective for treating moderate to severe cases.
- Excimer Laser: Delivers targeted UVB light to affected areas.
- Systemic Treatments: These are used for severe cases and involve oral or injected medications.
- Methotrexate: Reduces inflammation and skin cell production.
- Ciclosporin: Suppresses the immune system to reduce symptoms.
- Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system. Examples include adalimumab and etanercept.
- Natural Remedies: Some individuals find relief through natural treatments, though scientific evidence is limited.
- Aloe Vera: Has anti-inflammatory properties and can soothe the scalp.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Can help reduce itching and scaling when diluted and applied to the scalp.
- Tea Tree Oil: May reduce inflammation and prevent infections.
Lifestyle and Home Care
Managing scalp psoriasis also involves lifestyle changes and home care strategies:
- Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
- Moisturizing: Regularly moisturizing the scalp can prevent dryness and reduce itching.
- Gentle Hair Care: Avoid harsh shampoos and hair treatments that can irritate the scalp. Use a gentle, fragrance-free shampoo and avoid excessive scratching.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can support overall skin health.
Future Directions in Treatment
Research continues to advance in the field of psoriasis treatment, with promising developments in targeted therapies and personalized medicine. New biologics and small-molecule drugs offer hope for more effective and tailored treatments with fewer side effects.
Comparison Chart of Scalp Psoriasis Treatments
| Treatment | Form | Application Frequency | Main Benefits | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Cream, ointment | Daily | Reduces inflammation and itching | Skin thinning, irritation |
| Vitamin D Analogues | Cream, ointment | Daily | Slows skin cell growth | Skin irritation |
| Coal Tar | Shampoo, solution | 2-3 times weekly | Reduces scaling and inflammation | Staining, strong odor |
| Salicylic Acid | Shampoo, gel | Daily | Removes scales | Skin irritation |
| Tazarotene | Gel | Daily | Slows skin cell growth | Skin irritation, dryness |
| Methotrexate | Oral | Weekly | Reduces inflammation | Liver damage, nausea |
| Cyclosporine | Oral | Daily | Suppresses immune system | Kidney damage, high blood pressure |
| Biologics | Injectable | Bi-weekly/monthly | Targets specific immune pathways | Risk of infection |
| UVB Phototherapy | Light therapy | 2-3 times weekly | Reduces inflammation and scaling | Skin aging, burning |
| Excimer Laser | Laser therapy | Weekly | Targets specific plaques | Redness, blistering |
Q&A
Q: What is the most effective treatment for scalp psoriasis?
A: The most effective treatment varies from person to person. Topical corticosteroids are often the first choice, but biologics and phototherapy can be very effective for severe cases.
Q: Can scalp psoriasis be cured?
A: There is no cure for scalp psoriasis, but with the right treatment plan, symptoms can be managed effectively, and flare-ups can be minimized.
Q: Are there any natural remedies for scalp psoriasis?
A: Yes, natural remedies such as aloe vera, apple cider vinegar, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce symptoms. However, they should be used in conjunction with prescribed treatments.
Conclusion
Scalp psoriasis is a manageable condition with the right treatment and care. By understanding the causes and exploring various treatment options, individuals can find relief and improve their quality of life. Regular consultation with healthcare providers, combined with lifestyle changes and home care, can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment, there is hope for even more effective solutions in the future.
References







Recent Comments