Comprehensive Insights into Atopic Dermatitis: Symptoms, Treatments, and Impact
Atopic dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition affecting millions worldwide. Characterized by itchy, red, and swollen skin, AD significantly impacts quality of life and requires a multifaceted treatment approach.
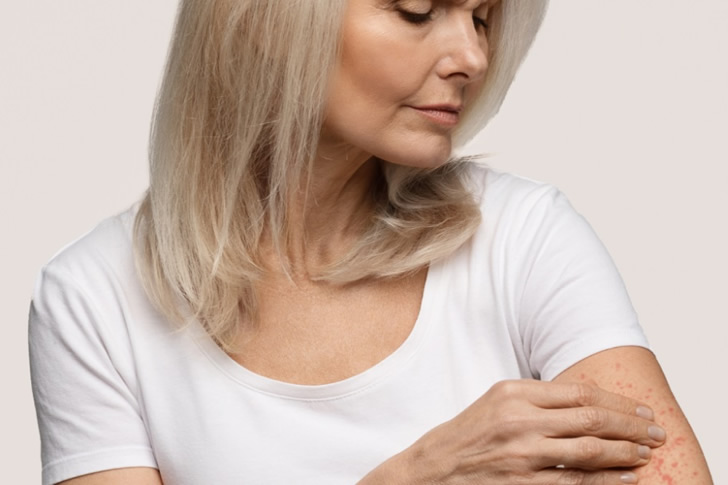

What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term skin disorder that causes dry skin, intense itching, and a red, swollen rash. It is most common in children but can persist into adulthood or start in older age. The condition is part of what’s known as the atopic triad (which includes asthma and hay fever), suggesting a link to allergic conditions.
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
Genetic Factors
- Family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever
- Mutations in the FLG gene affecting the skin barrier
Environmental Triggers
- Pollen, dust mites, pet dander
- Cold weather, dry air, and pollution
Immune System Dysregulation
- Overactive immune response leading to skin inflammation
Signs and Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
The signs and symptoms of atopic dermatitis can vary widely from person to person. Here are ten common indicators:
| Sign/Symptom | Description | Common Age of Onset |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Skin | Skin that is often rough and dry, lacking moisture | Any age |
| Itching | Intense itching, which may be more severe at night | Any age |
| Red Rashes | Reddish patches that may swell or feel tender | Infants |
| Scaly Skin | Skin appears scaly or with crusty, leathery textures | Any age |
| Oozing | Fluid may ooze from affected areas during flare-ups | Any age |
| Thickened Skin | Chronic scratching leads to thicker skin areas | Over time |
| Pigmentation Changes | Skin color may change, getting lighter or darker | Over time |
| Blisters | Small, fluid-filled blisters may develop | Less common |
| Sleep Disturbances | The intense itch can disrupt sleep | Any age |
| Ear Discharge | If eczema affects the ear, a discharge may be present | Rare |
Atopic Dermatitis in Seniors
- Increased Sensitivity: Older skin is thinner and may be more susceptible to irritations and infections.
- Complications: Seniors with atopic dermatitis are at higher risk of skin infections due to a weakened immune system.
- Management Challenges: Treatment in seniors may be complicated by other health conditions and medications.
Exploring Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis
Effective management of atopic dermatitis involves a combination of lifestyle changes, skin care routines, and medical treatments:
- Emollients (Moisturizers): Daily application to keep the skin moist and repair the skin barrier.
- Topical Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and itching during flare-ups.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Suppress the immune system’s activity to decrease inflammation.
- Biologic Drugs: Target specific parts of the immune system that contribute to inflammation.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to UVA or UVB rays can help reduce symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Can atopic dermatitis be cured?
- A: No, atopic dermatitis cannot be cured, but it can be managed with treatment.
- Q: Is atopic dermatitis contagious?
- A: No, the condition is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
- Q: What are the triggers for atopic dermatitis?
- A: Common triggers include dry skin, irritants, allergens, stress, and infections.
Preventative Measures
Skincare Routine
- Use Gentle, Fragrance-Free Products: Avoid soaps and cleansers that contain harsh chemicals.
- Maintain Skin Hydration: Apply moisturizers immediately after bathing.
Environmental Control
- Reduce Exposure to Allergens: Use air purifiers and dust-mite-proof covers.
- Maintain a Humid Environment: Use a humidifier to prevent dry skin.
2024 Latest Treatments For Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, continues to affect millions of people worldwide. In 2024, several new and promising treatments have emerged, offering hope for better management and improved quality of life for those suffering from this condition. These treatments range from innovative medications to advanced therapies designed to target the underlying causes of atopic dermatitis. Here, we explore four of the latest treatments that are making waves in the medical community.
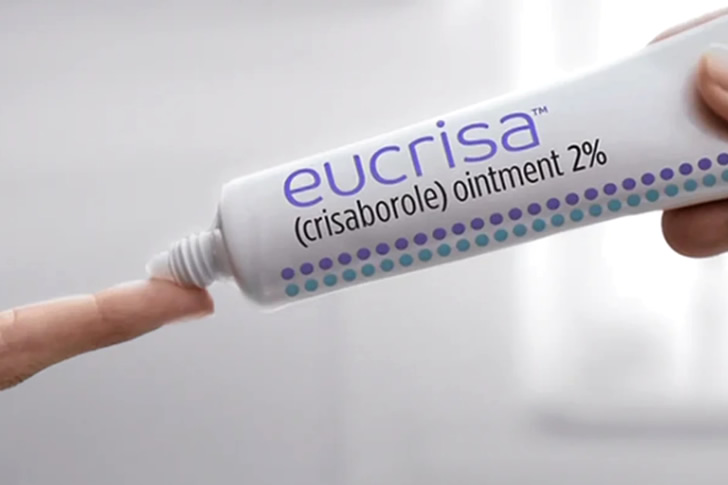

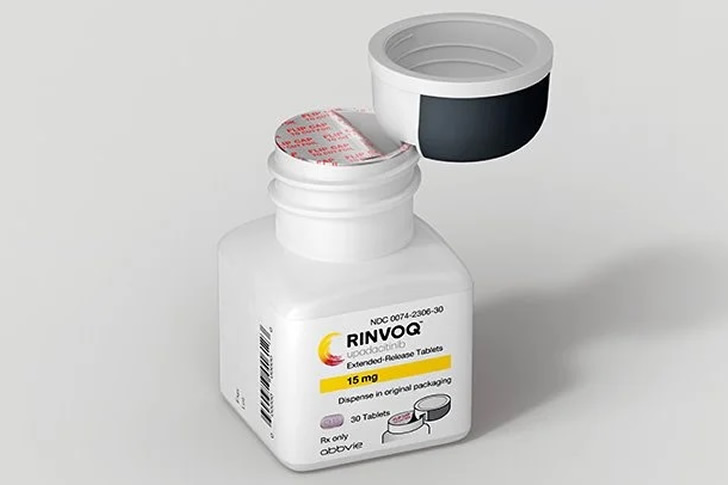
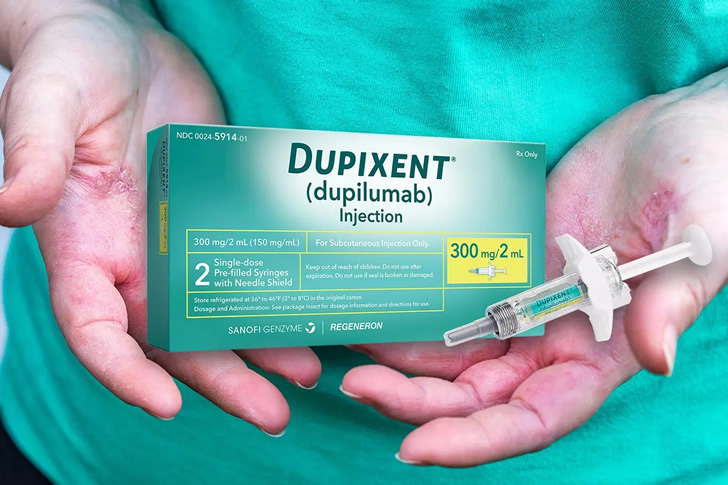
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis is a complex skin condition that requires a multifaceted approach to management. Understanding its symptoms and accessing effective treatments can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Continued research and patient education are crucial in the ongoing battle against this challenging condition.
References







Recent Comments