Effective Strategies for Managing Your Psoriasis
Psoriasis affects millions globally, understanding this chronic condition and its treatments is essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
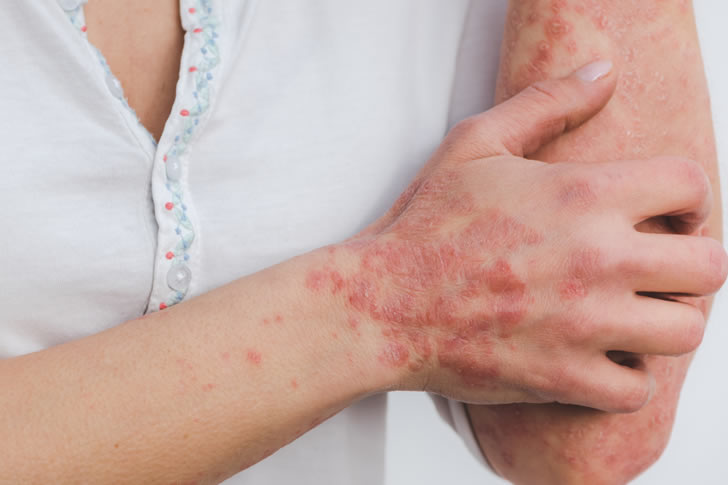
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each with unique characteristics:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterized by raised, red patches covered with a silvery white buildup of dead skin cells.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Small, dot-like lesions that often start in childhood or young adulthood.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Red, shiny lesions that appear in skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts.
- Pustular Psoriasis: White pustules (blisters of noninfectious pus) surrounded by red skin.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A particularly severe form, causing widespread redness and shedding of the skin over large areas of the body.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an immune system problem that causes skin cells to regenerate too quickly. Genetic and environmental factors, including stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, and infections, can trigger or worsen the condition.
How to Treat Psoriasis
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against psoriasis. These include:
- Corticosteroids: Anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce swelling and redness.
- Vitamin D Analogues: Slow down the growth of skin cells.
- Retinoids: Normalize DNA activity in skin cells and reduce inflammation.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Suppress the immune response to reduce inflammation.
- Coal Tar: Reduces scaling, itching, and inflammation.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision. Types include:
- UVB Phototherapy: Uses ultraviolet B light.
- PUVA Therapy: Combines a drug called psoralen with ultraviolet A light.
- Excimer Laser: Targets specific areas of the skin with high doses of UVB light.
Systemic Treatments
For moderate to severe psoriasis, systemic treatments are used. These affect the entire body and include:
- Methotrexate: Slows down cell growth and reduces inflammation.
- Cyclosporine: Suppresses the immune system.
- Biologic Agents: Target specific parts of the immune system. Examples include adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab.
- Oral Retinoids: Used for severe cases, but not commonly prescribed due to side effects.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Lifestyle changes and home remedies can also help manage psoriasis symptoms:
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated can reduce dryness and scaling.
- Take Warm Baths: Adding colloidal oatmeal or Epsom salts can help soothe itching.
- Reduce Stress: Stress management techniques such as yoga and meditation can help prevent flare-ups.
- Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers, such as certain foods, alcohol, and smoking, can help manage symptoms.
- Healthy Diet: Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can improve overall health and potentially reduce psoriasis severity.
Statistics and Facts
- According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, more than 8 million Americans have psoriasis.
- About 30% of people with psoriasis also develop psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain and swelling.
- Psoriasis can develop at any age, but it most commonly appears between the ages of 15 and 35.
- The World Health Organization estimates that around 2-3% of the global population is affected by psoriasis.
The Impact of Psoriasis on Quality of Life
Psoriasis can significantly affect quality of life, causing physical discomfort, emotional distress, and social isolation. Many patients experience depression and anxiety due to the visibility of their condition. It’s important for individuals with psoriasis to seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and mental health counselors.
Ongoing Research and Future Treatments
Research into new treatments for psoriasis is ongoing. Recent advancements include:
- Biologics: Newer biologic drugs that target specific pathways in the immune system with fewer side effects.
- JAK Inhibitors: A new class of oral medication that can reduce inflammation by inhibiting certain enzymes.
- Gene Therapy: Experimental treatments aiming to correct the underlying genetic causes of psoriasis.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a complex and chronic condition that requires a multifaceted treatment approach. By understanding the types of psoriasis, recognizing the triggers, and exploring various treatment options, individuals can effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Staying informed about new research and treatments can also provide hope and relief for those living with psoriasis.







Recent Comments